
2026 Class 8 Truck Market
January 2026
Updated January 26, 2026
Infrastructure and Construction Support
Vocational Class 8 demand remains soft entering 2026, with weakness persisting across construction, energy, and other cyclical end markets. Infrastructure-, utility-, and data-center-related activity continues to provide a modest baseline of demand, but execution remains uneven as public project timelines slip and elevated labor, material, and financing costs constrain momentum.
OEMs report that vocational inventories remain elevated and continue to correct more slowly than tractor inventories. Vocational units still represent an outsized share of total Class 8 stock relative to historical norms, particularly in construction- and energy-linked configurations. In response, manufacturers have carried production restraint into early 2026 to work down excess inventory. Despite longer-term infrastructure funding support, near-term vocational demand remains subdued and insufficient to drive a broader recovery.
Production and Backlogs
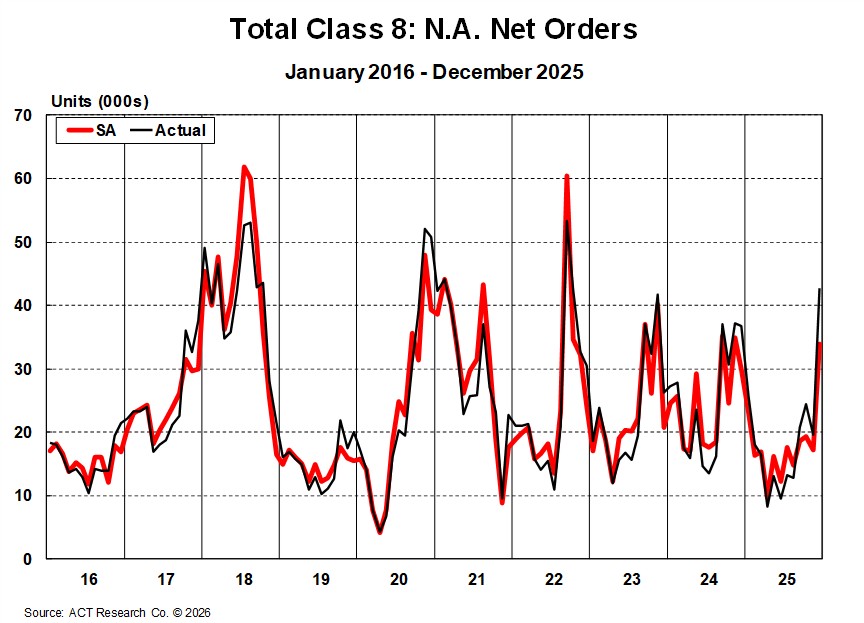
Class 8 production remains constrained entering 2026 as OEMs continue to align output with cautious order intake and margin protection priorities. While December orders surged late in the year, ACT Research views that activity as a catch-up event rather than confirmation of sustained momentum, reinforcing the need for continued production discipline.
Backlogs expanded modestly following the late-2025 order spike but remain historically low on a seasonally adjusted basis. The backlog-to-build (BL/BU) ratio continues to signal limited forward visibility despite some improvement in orderboards. Retail sales remain below replacement levels, supporting ongoing contraction in the active tractor population. Tractor inventories are approaching healthier alignment, while vocational inventories remain elevated and slower to normalize.
Regulatory Shifts
EPA 2027 remains the most influential regulatory variable shaping the 2026 outlook. January updates reinforce expectations that the EPA will retain core low-NOx technology requirements while revising or removing extended warranty and useful-life provisions. This improved clarity has reduced regulatory uncertainty but confirms that higher equipment prices in 2027 are increasingly likely. As a result, prebuy behavior remains measured, constrained by weak carrier profitability and elevated capital costs.
At the same time, §232 tariffs on heavy vehicles and major components are fully embedded in OEM pricing. These tariffs continue to materially increase acquisition costs—particularly for Mexico-sourced units—adding thousands of dollars per truck before financing, insurance, and compliance expenses. Combined with higher interest rates and compressed margins, tariff-driven inflation remains a significant constraint on fleet capital planning entering 2026.
Capacity Rebalancing
The Class 8 sector continues its gradual move toward balance as production discipline and sub-replacement sales drive accelerating capacity contraction. Tractor inventories have improved meaningfully following extended production cuts, but vocational inventories remain elevated and account for a disproportionate share of Class 8 stock.
In the used market, demand remains soft alongside uneven freight conditions, and pricing continues to face downward pressure. Newer equipment is holding value better than older units, but overall secondary-market pricing remains weak. While retirements are increasing and capacity contraction is clearly underway, total capacity still exceeds freight demand, anchoring new Class 8 purchases primarily to replacement needs.
Moderate Growth in Orders
Class 8 order activity entering 2026 reflects a market transitioning off the bottom rather than one in full recovery. December orders rebounded sharply, driven by improved regulatory clarity, weather-driven rate strength, and deferred replacement demand, but underlying fundamentals remain fragile.
Cancellations remain relatively contained, suggesting fleets are maintaining commitments rather than pulling back further. OEMs continue to manage production deliberately, prioritizing margin protection and backlog alignment as they open 2026 build slots cautiously. Absent sustained improvement in freight demand and carrier profitability, ACT Research expects Class 8 demand to remain near replacement levels through early 2026.
Economic Tailwinds and Risks
Infrastructure spending remains a longer-term tailwind, but near-term economic pressures continue to dominate the outlook. Tariff-driven cost inflation, lingering policy uncertainty, and elevated financing costs have created one of the most challenging operating environments for carriers in decades. Freight-intensive sectors—including housing, manufacturing, and energy—remain soft, while consumer-related shipments continue to reflect uneven post–pre-tariff demand patterns.
Smaller carriers remain particularly vulnerable amid tight credit conditions, rising operating costs, and limited pricing power. As fleets move through early 2026, priorities remain centered on cost containment, replacement timing, and liquidity preservation. A more durable recovery in Class 8 demand will depend on sustained freight stabilization, continued capacity contraction, and clearer policy conditions as 2026 unfolds.

Want more data?
ACT’s commercial vehicle forecast delivers the most reliable, forward-looking insight into where Class 8 truck sales are headed—helping you anticipate shifts, plan with confidence, and stay ahead of the market.